APAC is fastest growing market for latent TB detection in a global scenario. China, India, and Japan are three major contributors to the growth of the market. China led the APAC market. China is a country with a vast population and has flourished healthcare infrastructure, with rapid growth in communication. Tuberculosis is leading infectious disease and prevention is essential to TB control. As per the WHO, around 833,000 people fell ill with TB in china in 2019. China accounts for 10% of the global burden of TB with 400 million people having latent TB. Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection can remain inactive (latent) for months or years without detection. Advanced tuberculosis tests aid in the detection of latent TB infection can significantly reduce the risk of TB disease and can help prevent new outbreaks from recent transmission. New latent TB test kits, known as IGRA, provide more accurate results than tuberculin skin test. The country has launched the Chinese Infectious and Endemic Disease Control (IEDC) TB Project to control the TB infection. The IEDC project achieved huge success. As a result, between 1990 and 2000 the number of people with TB declined by 36.1%. However, despite the achievements of the IEDC project there were still problems with the TB control program in China. China still had one of the highest TB burdens in the world. The rate of TB in poor rural areas was three times higher than in the economically developed urban areas. China is still among the 30 high-burden tuberculosis countries in the world, and TB remains a public health concern. Increased coverage and quality of diagnosis, treatment for people infected with TB and latent TB is essential for fighting the battle against TB. Thus, increasing incidences of TB, rising government support are driving the growth of the advanced test, such as latent TB detection.
In case of COVID-19, APAC is highly affected specially India. The COVID-19 pandemic has put a major strain on the health systems of many countries around the world and may have negatively affected the delivery of TB services to vulnerable populations. The COVID-19 pandemic threatens to reverse progress in reducing the burden of TB infection in the region. The global number of TB deaths could increase by around 0.2–0.4 million in 2020, if health services are remained disrupted. India, Indonesia, the Philippines, and South Africa account for 44% of global TB cases, and large drops were reported in number of people diagnosed with TB between January and June 2020 due to interrupted healthcare services. The economic impact of the pandemic is predicted to worsen two of the key determinants of TB incidence: GDP per capita and undernutrition. Apart from this, lack of detection in TB cases due to lack of resources is negatively impacting the growth of the market. Many countries have reported the use of GeneXpert machines for COVID-19 testing instead of TB diagnosis, reassignment of staff in national TB programs to COVID-19 related duties and reallocation of budgets are further worsening the situation. In order to bring back the progress made in recent years, it is important to provide additional resources to reduce the number of unknown people with TB.

Strategic insights for the Asia Pacific Latent TB Detection provides data-driven analysis of the industry landscape, including current trends, key players, and regional nuances. These insights offer actionable recommendations, enabling readers to differentiate themselves from competitors by identifying untapped segments or developing unique value propositions. Leveraging data analytics, these insights help industry players anticipate the market shifts, whether investors, manufacturers, or other stakeholders. A future-oriented perspective is essential, helping stakeholders anticipate market shifts and position themselves for long-term success in this dynamic region. Ultimately, effective strategic insights empower readers to make informed decisions that drive profitability and achieve their business objectives within the market.
| Report Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
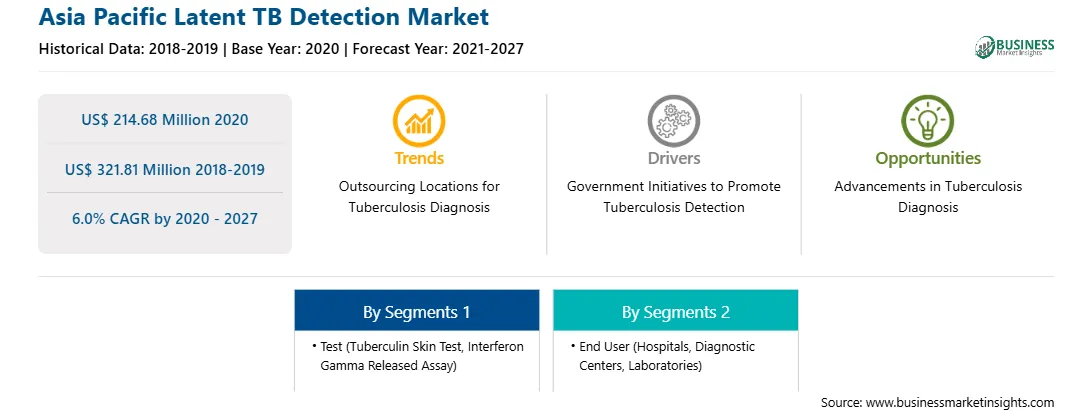
| Market size in 2020 | US$ 214.68 Million |
| Market Size by 2027 | US$ 321.81 Million |
| Global CAGR (2020 - 2027) | 6.0% |
| Historical Data | 2018-2019 |
| Forecast period | 2021-2027 |
| Segments Covered |
By Test
|
| Regions and Countries Covered | Asia-Pacific
|
| Market leaders and key company profiles |
The geographic scope of the Asia Pacific Latent TB Detection refers to the specific areas in which a business operates and competes. Understanding local distinctions, such as diverse consumer preferences (e.g., demand for specific plug types or battery backup durations), varying economic conditions, and regulatory environments, is crucial for tailoring strategies to specific markets. Businesses can expand their reach by identifying underserved areas or adapting their offerings to meet local demands. A clear market focus allows for more effective resource allocation, targeted marketing campaigns, and better positioning against local competitors, ultimately driving growth in those targeted areas.
The APAC latent TB detection market is expected to grow from US$ 214.68 million in 2020 to US$ 321.81 million by 2027; it is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 6.0% from 2020 to 2027. Tuberculosis (TB) can stay dormant for years before developing into an active TB disease. This condition is known as latent TB. Diagnosis of latent TB is imperative, as it will develop into infectious TB disease when the immune system becomes weak. The World Health Organization (WHO) stated that a total of 1.4 million people died from TB in 2019, making TB one of the top 10 causes of mortality in the region. The data also stated that in 2019 TB affected millions of people in the region, of which 56% were adult males, 32% were adult females, and 12% were children. The disease is prevalent in all age groups across the region. India, Indonesia, China, the Philippines, Pakistan, and Bangladesh are among the countries that are highly affected with TB across the region. Therefore, the high prevalence of TB is driving the need for TB tests, in turn, propelling the growth of the APAC latent TD detection market.
In terms of test, the tuberculin skin test (TST) segment accounted for the largest share of the APAC latent TB detection market in 2019. In terms of end user, the hospitals segment held a larger market share of the APAC latent TB detection market in 2019.
A few major primary and secondary sources referred to for preparing this report on the APAC latent TB detection market are company websites, annual reports, financial reports, national government documents, and statistical database, among others. Major companies listed in the report are Abbott; ARKRAY, Inc.; BD; bioMerieux SA; F. HOFFMANN-LA ROCHE LTD.; Lionex GmbH; Oxford Immunotec Ltd; QIAGEN; and Serum Institute of India Pvt. Ltd.
The Asia Pacific Latent TB Detection Market is valued at US$ 214.68 Million in 2020, it is projected to reach US$ 321.81 Million by 2027.
As per our report Asia Pacific Latent TB Detection Market, the market size is valued at US$ 214.68 Million in 2020, projecting it to reach US$ 321.81 Million by 2027. This translates to a CAGR of approximately 6.0% during the forecast period.
The Asia Pacific Latent TB Detection Market report typically cover these key segments-
The historic period, base year, and forecast period can vary slightly depending on the specific market research report. However, for the Asia Pacific Latent TB Detection Market report:
The Asia Pacific Latent TB Detection Market is populated by several key players, each contributing to its growth and innovation. Some of the major players include:
The Asia Pacific Latent TB Detection Market report is valuable for diverse stakeholders, including:
Essentially, anyone involved in or considering involvement in the Asia Pacific Latent TB Detection Market value chain can benefit from the information contained in a comprehensive market report.